Using Figure 6.4 as a model, illustrate the operation of \(\textsc{Heapsort}\) on the array \(A = \langle 5, 13, 2, 25, 7, 17, 20, 8, 4 \rangle\).
To understand how heapsort works, we need to follow two phases. First, we build a max-heap from the unsorted array. Second, we repeatedly extract the maximum element (which is always at the root) and place it at the end of the array, then restore the heap property for the remaining elements.
Let’s trace through the algorithm step by step. The initial array is \(\langle 5, 13, 2, 25, 7, 17, 20, 8, 4 \rangle\).
Phase 1: Building the max-heap
We start by calling \(\textsc{Build-Max-Heap}\), which processes nodes from \(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor = 4\) down to 1. After building the max-heap, we get:
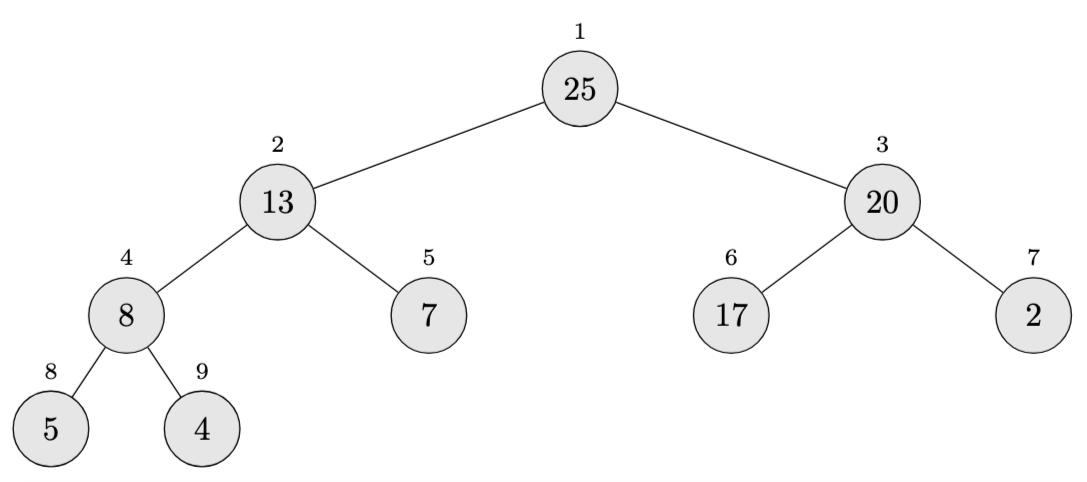
\[\langle 25, 13, 20, 8, 7, 17, 2, 5, 4 \rangle\]This represents a max-heap where:
- The root (25) is the largest element
- Each parent is greater than or equal to its children
Phase 2: Sorting
Now we repeatedly swap the root with the last element in the heap, decrease the heap size, and call \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}\) on the root.
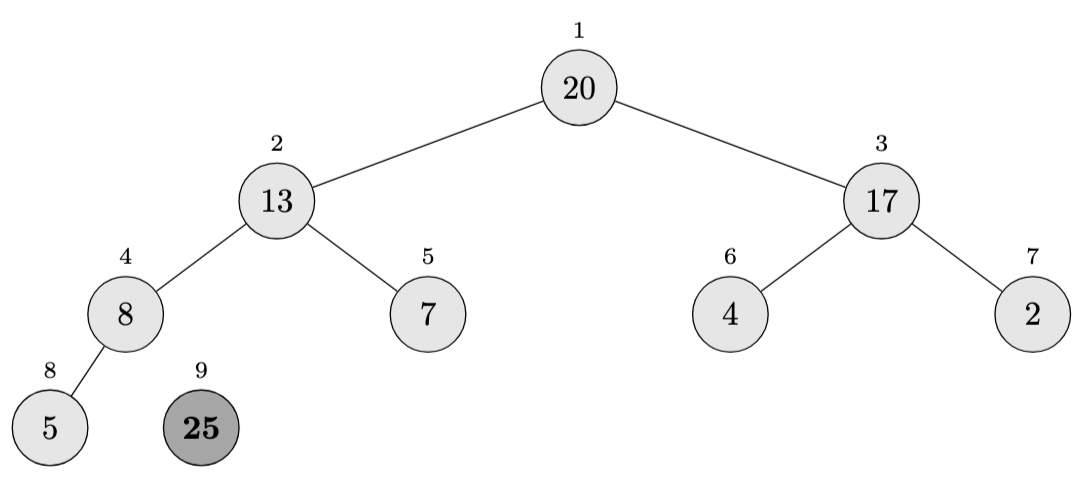
Iteration 1 (\(i = 9\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[9]\): \(\langle 4, 13, 20, 8, 7, 17, 2, 5, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 8
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 20, 13, 17, 8, 7, 4, 2, 5, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
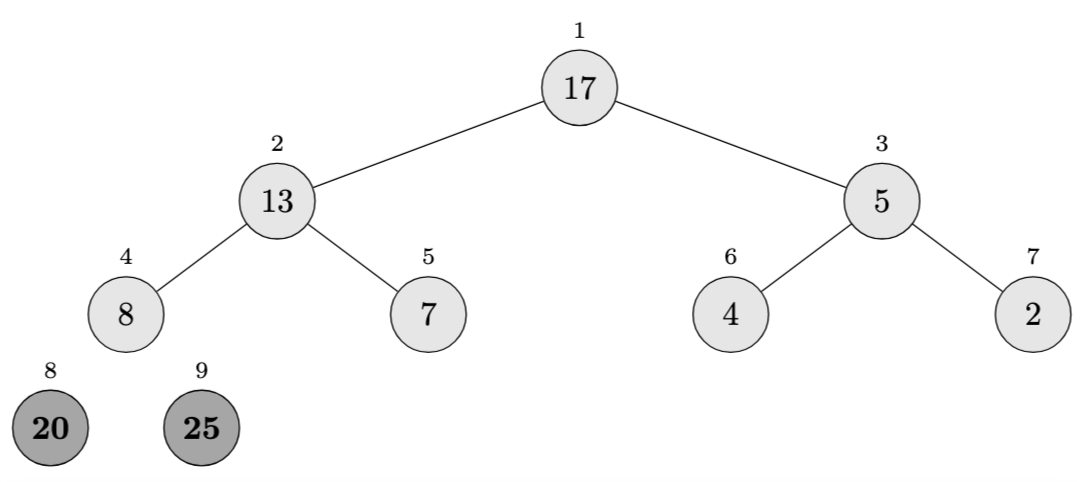
Iteration 2 (\(i = 8\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[8]\): \(\langle 5, 13, 17, 8, 7, 4, 2, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 7
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 17, 13, 5, 8, 7, 4, 2, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
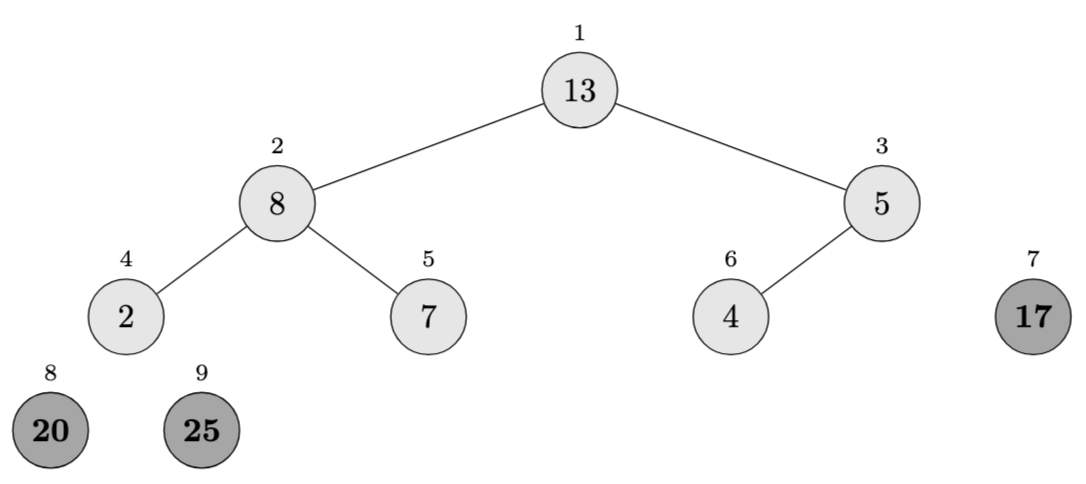
Iteration 3 (\(i = 7\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[7]\): \(\langle 2, 13, 5, 8, 7, 4, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 6
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 13, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
Iteration 4 (\(i = 6\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[6]\): \(\langle 4, 8, 5, 2, 7, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 5
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 8, 7, 5, 2, 4, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
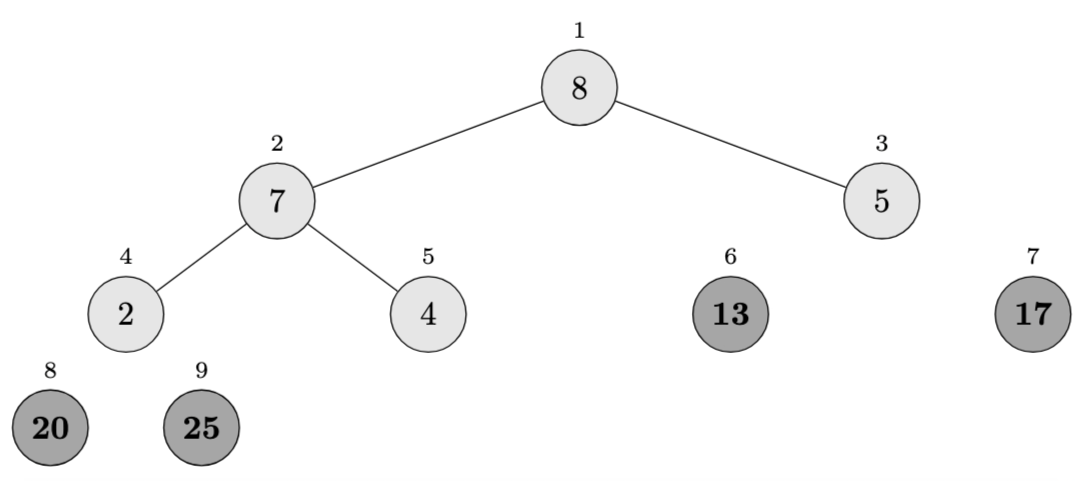
Iteration 5 (\(i = 5\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[5]\): \(\langle 4, 7, 5, 2, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 4
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 7, 4, 5, 2, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
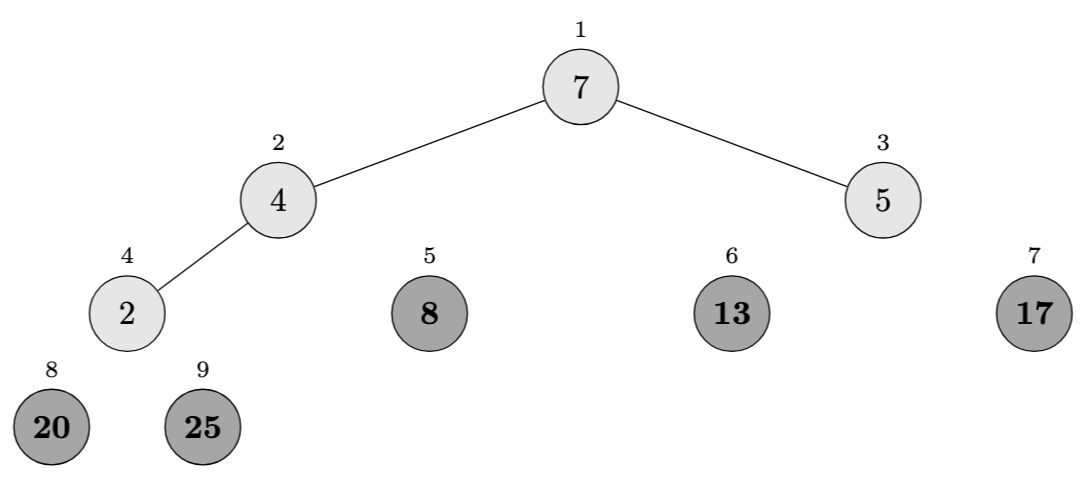
Iteration 6 (\(i = 4\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[4]\): \(\langle 2, 4, 5, \mathbf{7}, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 3
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 5, 4, 2, \mathbf{7}, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
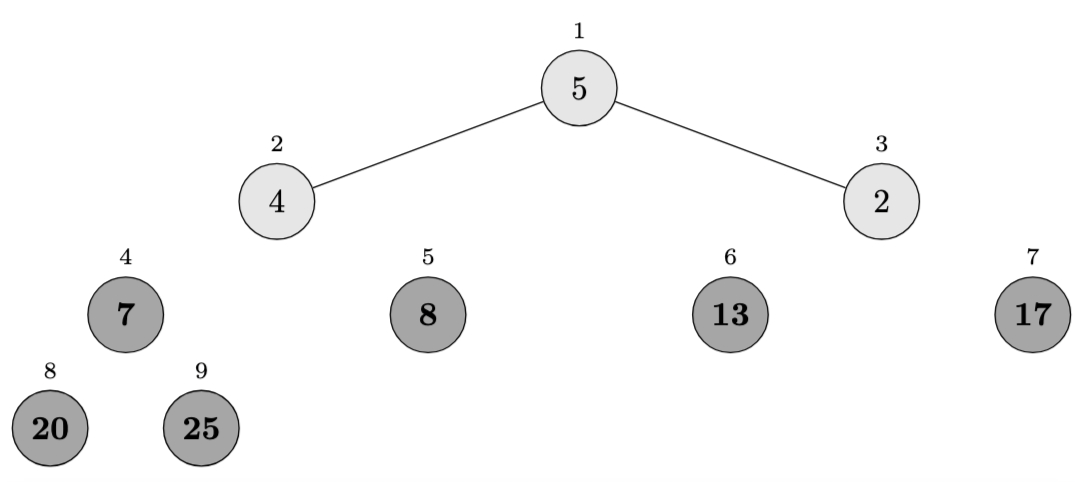
Iteration 7 (\(i = 3\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[3]\): \(\langle 2, 4, \mathbf{5}, \mathbf{7}, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Heap size becomes 2
- After \(\textsc{Max-Heapify}(A, 1)\): \(\langle 4, 2, \mathbf{5}, \mathbf{7}, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
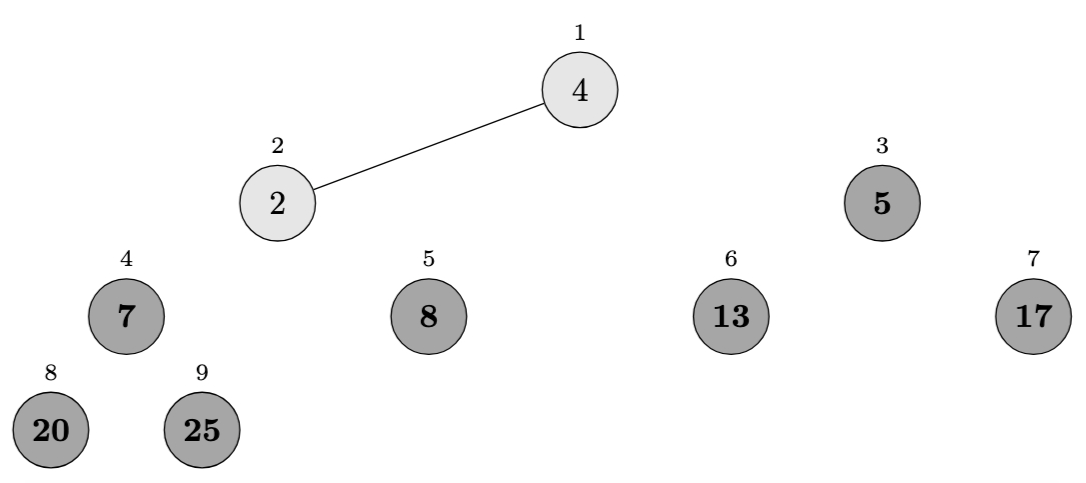
Iteration 8 (\(i = 2\)):
- Swap \(A[1]\) and \(A[2]\): \(\langle 2, \mathbf{4}, \mathbf{5}, \mathbf{7}, \mathbf{8}, \mathbf{13}, \mathbf{17}, \mathbf{20}, \mathbf{25} \rangle\)
- Loop terminates
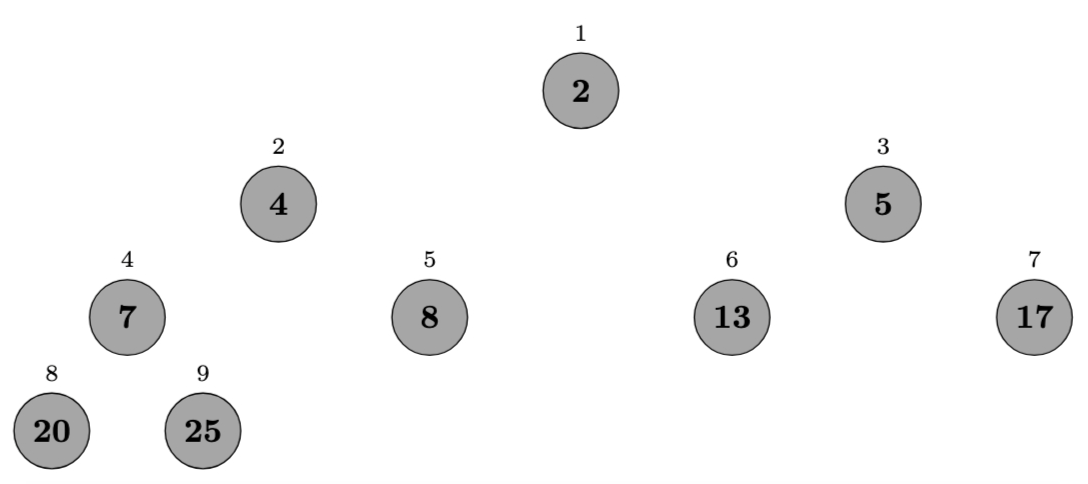
Final sorted array: \(\langle 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 13, 17, 20, 25 \rangle\)